Cutting Parameters
Cutting parameters are the key settings used to control and optimize the machining process when working with materials like steel, aluminum, cast iron, or stainless steel. They determine how efficiently and accurately a cutting tool removes material, directly affecting the surface finish, tool life, and production speed.
Turning inserts are replaceable cutting tools used in lathes to machine materials by removing metal through controlled cutting speeds, feeds, and depths for desired finish and chip control.
Cutting Speed: Steel 150–250 m/min, Aluminum 500–1000 m/min
Feed Rate: 0.1–0.5 mm/rev
Depth of Cut: 1–6 mm
Best Practices: Optimize for chip control & finish.


Milling holders are precision devices that secure milling tools during machining, while milling inserts are replaceable cutting edges—typically carbide—used to efficiently remove material, achieve desired finishes, and optimize productivity in milling operations.
Cutting Speed: Steel 60–120 m/min, Aluminum 300–600 m/min
Feed per Tooth: 0.05–0.3 mm
Depth of Cut: 0.5–5 mm
Best Practices: Match insert type to cutter size.


Grooving inserts are specialized cutting tools used in machining operations to create precise grooves or channels—internal or external—on a workpiece, essential for features like O-ring seats, retaining clips, or thread reliefs in components.
Feed Rate: 0.06–0.24 mm/rev
Depth of Cut: Minimal for chip control
Technique: Plunge sides first, slower side feed.


Drilling inserts are replaceable cutting edges—typically carbide—mounted onto drill bodies for efficient, precise hole-making in machining, allowing rapid tool changes and consistent performance.
Cutting Speed: Based on diameter & material
Depth of Cut: Per pass, per drill length
Tip: Watch torque & thrust on hard materials.
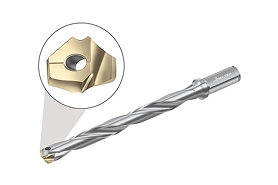

Threading inserts are specialized cutting tool inserts designed for threading operations in CNC turning and machining. They have specific geometries and edge designs to accurately cut internal or external threads with high precision and consistency.
Feed: Matches thread pitch
Depth of Cut: Smaller final passes for finish
Passes: Multiple passes for tool life


Solid carbide rods are cylindrical bars made entirely of tungsten carbide, known for their exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and high-temperature stability, which make them ideal for manufacturing precision cutting tools such as end mills, drills, reamers, and custom machining tools.
High cutting speeds due to hardness
Coolant holes improve heat dissipation
Precision-ground for tolerance & reliability


Special tools in machining refer to custom-designed or specially engineered cutting tools tailored to perform specific, often complex, machining operations or to meet unique production requirements.
Cutting parameters vary by material
Used for advanced materials & superalloys
Requires optimized speed & feed


Torque solutions generally refer to specialized tools and systems designed to apply precise torque values to fasteners for assembly, maintenance, and industrial applications
Torque ensures correct insert screw tightening
Example: Milling inserts require 0.5–4.5 Nm
Always use a torque wrench


| Parameter | Turning Inserts | Milling Holders / Inserts | Grooving Inserts | Drilling Inserts | Threading Inserts | Special Tools |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cutting Speed (Vc) | 150–1,000 m/min | 60–600 m/min | Material-based | Varies (drill & material) | Material-based | Variable (custom) |
| Feed Rate | 0.1–0.5 mm/rev | 0.05–0.3 mm/tooth | 0.06–0.24 mm/rev | Calculated from Vc & D | Matches thread pitch | Variable (application) |
| Depth of Cut (ap) | 1–6 mm | 0.5–5 mm | Minimal / controlled | Drill size & pass-based | 0.025–0.05 mm (final pass) | Application-specific |
| Tool Geometry | Nose angle / nose radius | Diameter / flutes / coating | Groove width / depth | Point, angle, flute form | Thread profile & lead | Custom geometry |
| Torque | N/A | Holder/insert screw torque | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
